When generating hydropower, the head is the distance that a given water source has to fall before the point where power is generated. Ultimately the force responsible for hydropower is gravity, so a hydroelectricity plant with a tall/high head can produce more power than a similar plant with a short/low head. In short, for a given water flow, a larger head will be converted into greater kinetic energy. That energy is then harnessed by a water wheel or water turbine to create usable hydropower.
Fabrics
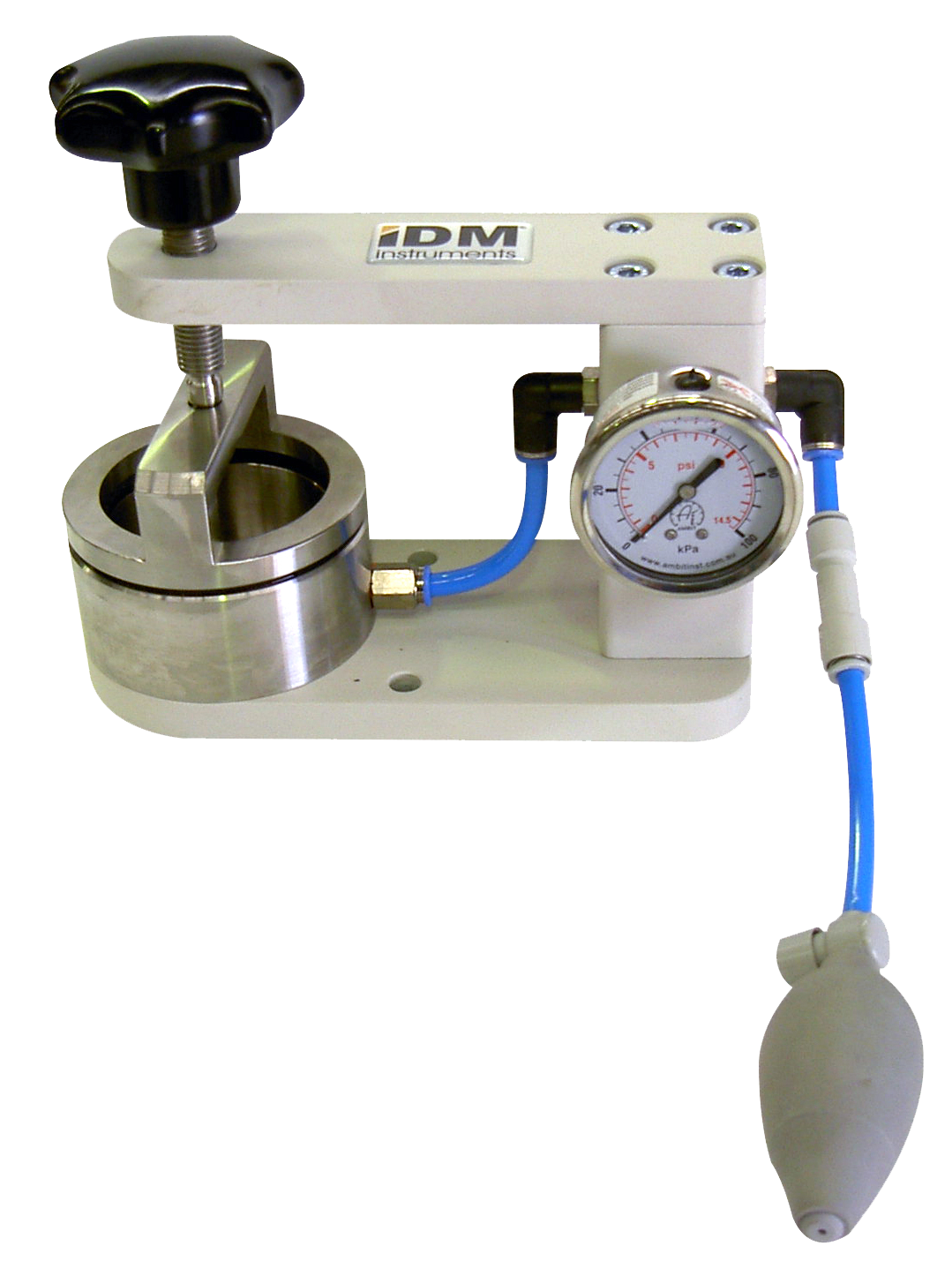
Hydrostatic head is also used as a measure of the waterproofing of a fabric, commonly in clothing and equipment used for outdoor recreation. It is measured as a length (typically millimetres), representing the maximum height of a vertical column of water that could be placed on top of the fabric before water started seeping through the weave. Thus a fabric with a hydrostatic head rating of 5000 mm could hold back a column of water five metres high, but no more.
Notes
See also
- Hydraulic head for a more technical description of the physical principle of hydraulics
- Tent and waterproofing, as hydrostatic head is used as a measurement of waterproofness
References
- U.S. Bureau of Reclamation: Glossary (See “Head”)
- U.S. Minerals Management Service: Glossary (See “Hydraulic head”]
- Society of Petrophysicists & Well Log Analysts: Glossary (See “Hydraulic head”)