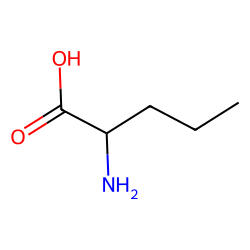
Norvaline (abbreviated as Nva) is an amino acid with the formula CH3(CH2)2CH(NH2)CO2H. The compound is a structural analog of valeric acid and also an isomer of the more common amino acid valine. Like most other α-amino acids, norvaline is chiral. It is a white, water-soluble solid.
Occurrence
Norvaline is a non-proteinogenic unbranched-chain amino acid. It has previously been reported to be a natural component of an antifungal peptide of Bacillus subtilis. Norvaline and other modified unbranched chain amino acids have received attention because they appear to be incorporated in some recombinant proteins found in E. coli. Its biosynthesis has been examined. The incorporation of Nva into peptides reflects the imperfect selectivity of the associated aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. In Miller–Urey experiments probing prebiotic synthesis of amino acids, norvaline, but also norleucine, are produced.
Nomenclature
Norvaline and norleucine (one hydrocarbon group longer) both possess the nor- prefix for historical reason, despite current conventional usage of the prefix to denote a missing hydrocarbon group (under which they would theoretically be called "dihomoalanine" and "trihomoalanine"). The name is not systematic, and the IUPAC/IUB Joint Commission on Nomenclature recommends that this name should be abandoned and the systematic name should be used.
Potential uses
Norvaline is used as a dietary supplement for bodybuilding. Recently, it was suggested in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
References